

|
PAPPDFName:
with \( \theta \) and p denoting the shape parameters. The Polya-Aeppli distribution can be derived as a model for the number of objects where the objects occur in clusters, the clusters follow a Poisson distribution with shape parameter \( \theta \), and the number of objects within a cluster follows a geometric distribution with shape parameter p. For this reason, this distribution is sometimes referred to as a geometric Poisson distribution Note that there are a number of alternative parameterizations of this distribution in the literature. The parameterization used above is the one given in Johnson, Kotz, and Kemp. The moments of this distribution are:
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <x> is a non-negative integer variable, number, or parameter; <theta> is a positive number or parameter that specifies the first shape parameter; <p> is a positive number or parameter that specifies the second shape parameter; <y> is a variable or a parameter where the computed Polya-Aeppli pdf value is stored; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional.
LET Y = PAPPDF(X1,2,0.3) PLOT PAPPDF(X,2,0.3) FOR X = 0 1 20
LET THETA = <value> LET LAMBDA = <value> LET Y = POLYA AEPPLI RANDOM NUMBERS FOR I = 1 1 N
POLYA AEPPLI PROBABILITY PLOT Y
POLYA AEPPLI CHI-SQUARE GOODNESS OF FIT Y2 X2 To obtain the method of moments, the method of zero frequency and the mean, and the weighted discrepancies estimates of lambda and theta, enter the command
POLYA AEPPLI MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y2 X2 The method of moments estimators are:
\( \hat{p} = \frac{s^2 - \bar{x}} {s^2 + \bar{x}} \) with \( \bar{x} \) and s2 denoting the sample mean and sample variance, respectively. The method of zero frequency and sample mean estimators are:
\( \hat{p} = 1 - \frac{\hat{\theta}} {\bar{x}} \) with \( \bar{x} \) and f0 denoting the sample mean and sample frequency at x = 0, respectively. The method of the first two frequencies estimators are:
\( \hat{p} = -\frac{f_1}{f_0 \log(f_0/N)} \) with f0 and f1 denoting the sample frequency at x = 0 and x = 1, respectively. The maximum likelihood estimates are the solutions of the following two equations:
\( \bar{x} - \sum_{j=1}^{N}{\frac{f_{j}(j-1)\hat{P_{j-1}}} {N \hat{P_j}}} = 0 \) with fx and \( \hat{p}_{x} \) denoting the frequency at x and the Polya-Aeppli probaility mass function value at x, respectively. You can generate estimates of theta and p based on the maximum ppcc value or the minimum chi-square goodness of fit with the commands
LET THETA2 = <value> LET P1 = <value> LET P2 = <value> POLYA AEPPLI CHI-SQUARE PLOT Y POLYA AEPPLI CHI-SQUARE PLOT Y2 X2 POLYA AEPPLI CHI-SQUARE PLOT Y3 XLOW XHIGH POLYA AEPPLI PPCC PLOT Y POLYA AEPPLI PPCC PLOT Y2 X2 POLYA AEPPLI PPCC PLOT Y3 XLOW XHIGH The default values of p1 and p2 are 0.05 and 0.95, respectively. The default values of theta1 and theta2 are 1 and 25, respectively. Due to the discrete nature of the percent point function for discrete distributions, the ppcc plot will not be smooth. For that reason, if there is sufficient sample size the CHI-SQUARE PLOT (i.e., the minimum chi-square value) is typically preferred. However, it may sometimes be useful to perform one iteration of the PPCC PLOT to obtain a rough idea of an appropriate neighborhood for the shape parameters since the minimum chi-square statistic can generate extremely large values for non-optimal values of the shape parameter. Also, since the data is integer values, one of the binned forms is preferred for these commands.
Evans (1953), "Experimental Evidence Concerning Contagious Distributions in Ecology", Biometrika, 40, pp. 186-211. Johnson, Kotz, and Kemp (1992), "Univariate Discrete Distributions", Second Edition, Wiley, pp. 378-382.
let theta = 1.7
let lambda = 0.7
let y = polya aeppli random numbers for i = 1 1 500
.
let y3 xlow xhigh = integer frequency table y
class lower 0.5
class width 1
let amax = maximum y
let amax2 = amax + 0.5
class upper amax2
let y2 x2 = binned y
.
set write decimals 5
let k = minimum y
polya aeppli mle y
relative histogram y2 x2
limits freeze
pre-erase off
line color blue
plot pappdf(x,thetaml,pml) for x = 0 1 amax
limits
pre-erase on
line color black
let p = lambdaml
let theta = thetaml
polya aeppli chi-square goodness of fit y3 xlow xhigh
case asis
justification center
move 50 97
text Theta = ^thetaml, P = ^pml
move 50 93
text Minimum Chi-Square = ^minks, 95% CV = ^cutupp95
.
label case asis
x1label Lambda
y1label Minimum Chi-Square
let theta1 = 0.5
let theta2 = 5
let p1 = 0.1
let p2 = 0.9
polya aeppli chi-square plot y3 xlow xhigh
let theta = shape1
let p = shape2
polya aeppli chi-square goodness of fit y3 xlow xhigh
case asis
justification center
move 50 97
text Theta = ^theta, P = ^p
move 50 93
text Minimum Chi-Square = ^minks, 95% CV = ^cutupp95
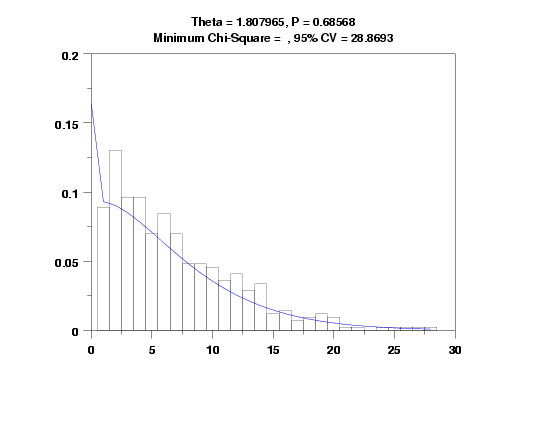
Polya-Aeppli Parameter Estimation
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 500
Sample Mean: 5.75200
Sample Standard Deviation: 5.38967
Sample Minimum: 0.00000
Sample Maximum: 28.00000
Sample First Frequency: 85.00000
Sample Second Frequency: 37.00000
Method of Moments:
Estimate of Theta: 1.90143
Estimate of P: 0.66943
Method of Zero Frequency and Mean:
Estimate of Theta: 1.77196
Estimate of P: 0.69194
Method of First Two Frequencies:
Estimate of Theta: 1.77196
Estimate of P: 0.24566
Method of Maximum Likelihood:
Estimate of Theta: 1.80797
Estimate of P: 0.68568
Chi-Square Goodness of Fit Test
Bin Frequency Variable: Y3
Bin Lower Boundary Variable: XLOW
Bin Upper Boundary Variable: XHIGH
H0: The distribution fits the data
Ha: The distribution does not fit the data
Distribution: POLYA AEPPLI
Shape Parameter 1: 1.80797
Shape Parameter 2: 0.68568
Summary Statistics:
Total Number of Observations: 500
Minimum Class Frequency 1
Number of Non-Empty Cells 21
Degress of Freedom 18
Sample Minimum: -0.50000
Sample Maximum: 28.50000
Sample Mean: 5.75200
Sample SD: 5.37741
Chi-Square Test Statistic Value: 13.10322
CDF Value: 0.21460
P-Value 0.78540
Percent Points of the Reference Distribution
-----------------------------------
Percent Point Value
-----------------------------------
0.0 = 0.000
50.0 = 17.338
75.0 = 21.605
90.0 = 25.989
95.0 = 28.869
97.5 = 31.526
99.0 = 34.805
99.5 = 37.156
Conclusions (Upper 1-Tailed Test)
----------------------------------------------
Alpha CDF Critical Value Conclusion
----------------------------------------------
10% 90% 25.989 Accept H0
5% 95% 28.869 Accept H0
2.5% 97.5% 31.526 Accept H0
1% 99% 34.805 Accept H0
|
Privacy
Policy/Security Notice
NIST is an agency of the U.S.
Commerce Department.
Date created: 06/20/2006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||