

|
MAXIMUM LIKELIHOODName:
For some distributions, maximum likelihood methods may have theoretical issues (e.g., the maximum likelihood solution may not exist) or numerical issues (e.g., non-convergence). As maximum likelihood methods are well documented in the statistical literature, we will not discuss them here. CONTINUOUS DISTRIBUTIONSFor some distributions, Dataplot will also generate estimates based on other methods. Specifically, for continuous distributions the following methods may also be used:
In some cases, these methods are used to obtain starting values. In other cases, they are used where maximum likehood methods are known to have performance issues. We distinguish the following types of data.
The Dataplot MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD command primarily supports case 1 (i.e., ungrouped, uncensored data). Censored data is supported for some distributions commonly used in reliability/lifetime applications. There is a distinction between censored and truncated data. The distinction is that for censored data the number of censored points is known while for truncated data the number of censored points is unknown. Censoring is common in life testing where we test a fixed known number of units. In this case, the censored data are those units that have not failed when the test is ended. On the other hand, an example of truncated data might be a sensor where we have a limit of detection (that is, there is a minimum level of something that must be present before the instrument can detect its presence). That is, for truncated data the number of truncated units is unknown. The following types of information may be reported by the maximum likelihood command:
At a minimum, point estimates will be reported. Items 2 - 4 depend on the specific distribution. For distributions where only point estimates are generated, the DISTRIBUTIONAL BOOTSTRAP command may be used to generate confidence intervals for the parameter estimates and for selected percentiles. The following distributions are currently supported.
DISCRETE DISTRIBUTIONSData for discrete data can be either raw data or in the form of a frequency table. Dataplot currently requires that frequency tables have equal group sizes (data will sometimes be reported with frequency tables with unequal group sizes, typically due to groups in the upper tail being combined).The following methods may be used to compute point estimates
where <DIST> is one of the supported distributions; <y> is the response variable; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This generates maximum likelihood estimates for the raw data (no grouping) case with no censoring.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <DIST> is one of the supported distributions; <y> is a variable containing frequencies; <x> is a variable containing the bin mid-points; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax is used for grouped (frequency table) data. The bins are assumed to have equal width.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <DIST> is one of the supported distributions; <y> is a variable containing frequencies; <xlow> is a variable containing the lower value for the bins; <xhigh> is a variable containing the upper value for the bins; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax is used for grouped (frequency table) data where the bins do not have equal width.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <DIST> is one of the supported distributions; <y> is the response variable; <x> is the censoring variable; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This is for the raw data (ungrouped) case with censoring. The censoring variable should contain 1's and 0's where 1 indicates a failure time and 0 indicates a censoring time.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <DIST> is one of the supported distributions; <y1> ... <yk> is a list of 1 to 30 response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax will perform maximum likelihood estimation for each of the listed response variables. Censoring is not supported for this syntax. The TO keyword can be used with this sytax (see Examples below).
LOGNORMAL MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y EXPONENTIAL MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y WEIBULL CENSORED MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y X WEIBULL MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y SUBSET TAG = 1 WEIBULL MULTIPLE MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y1 Y2 Y3 WEIBULL MULTIPLE MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Y1 TO Y5
To specify the minimum order statistic case, enter
To specify the maximum order statistic case, enter
The default is the minimum order statistic case for the Weibull distribution and the maximum order statistic case for the other distributions.
This will compute 17 select percentiles. If you would like to specify the specific percentiles, do something like the following
SET MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD PERCENTILES YPERC To turn off the percentile confidence limits, enter
By default, two-sided confidence intervals are generated for the percentiles. To specify lower one-sided intervals, enter
To specify upper one-sided intervals, enter
To reset two-sided intervals, enter
Note that one-sided percentiles are also one-sided tolerance intervals. See the tables above to determine which distributions support percentile confidence intervals. Confidence intervals for percentiles are by default 95% confidence intervals. To change the confidence level, enter the command
where <value> is typically 0.10, 0.05, or 0.01. By default, the percentile column (i.e., the first column in the table) is printed with 3 digits to the right of the decimal point. If you are generating percentiles that are close to zero or one (e.g., 0.00005), you may need to increase the number of digits. You can do this with the command
Bias correction can be specified for the following distributions
SET FRECHET BIAS CORRECTED <ON/OFF> SET GUMBEL BIAS CORRECTED <ON/OFF> SET WEIBULL BIAS CORRECTED <ON/OFF> The default is OFF for all of these.
SET WEIBULL MOMENTS <ON/OFF> SET WEIBULL L MOMENTS <ON/OFF> SET WEIBULL MODIFIED MOMENTS <ON/OFF> SET WEIBULL MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD <ON/OFF> The elemental percentiles and L moment methods are OFF and the others are ON by default. The maximum likelihood method is described in the Bury, Rhinne, and Cohen and Whitten references. The moment, modified moment and L moment methods are described in the Cohen and Whitten reference. The elemental percentile method is described in Castillo, et. al. Maximum likelihood for the 3-parameter Weibull can be problematic for small values of the shape parameter. Lawless proposed the profile method to address this. In this method, a grid of location values is created from the minimum value to zero. For each value on this grid, a 2-parameter Weibull is estimated via maximum likelihood. The value of the location parameter that generates the optimal 2-parameter Weibull estimates is the estimate of location for the 3-parameter Weibull distribution (the scale and shape are the estimates from the 2-parameter Weibull estimation). To specify the Lawless profile method be used for the maximum likelihood estimates, enter the command
To turn off the profile method, enter
By default, the grid is created from zero to the minimum of the data. If you want to restrict the location to something other than zero, then you can enter the command
That is, the grid will be created from
In the materials field, the Weibull distribution is typically
parameterized with a gauge length parameter (enter HELP WEIPDF for
details). This gauge length parameter modifies the value of the
scale parameter, but otherwise the estimation is equivalent to the
typical parameterization of the Weibull distribution. To utilize
the gauge length parameterization for the 3-parameter Weibull
estimation, enter the command
To specify the value of the gauge length, enter
SET LOGNORMAL MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD MINIMUM <value> SET GAMMA MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD METHOD <PROFILE/COHEN> SET GAMMA MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD MINIMUM <value>
To turn on the maximum likelihood estimation method (this is intended primarily for testing at this time), enter the command
SET GENERALIZED PARETO MLE START VALUES L MOMENTS SET GENERALIZED PARETO MLE START VALUES ELEMENTAL PERCENTILES SET GENERALIZED PARETO MLE START VALUES USER SPECIFIED The default is to use the elemental percentile estimates as the start values for the maximum likelihood method. If USER SPECIFIED is entered, you can specify the start values with the commands
LET GAMMASV = <value>
If available for a particular distribution, these will typically be documented in the PDF routine (e.g., NBPDF).
The PPCC PLOT and PROBABILITY PLOT commands document fitting parameters by maximizing the probability plot correlation coefficient. The PPCC PLOT has variants where you can minimize the Anderson-Darling, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, and chi-square goodness of fit statistic. The NORMAL PLOT, WEIBULL PLOT and FRECHET PLOT can be used for the normal, 2-parameter Weibull (minimum case), and 2-parameter Frechet (maximum case).
let n = size y let p = uniform order statistic medians for i = 1 1 n let gamma = 3.5; . Specify a starting value for the shape let scale = 10; . Specify a starting value for the scale fit y = weippf(p,gamma,0,scale) Be aware that the standard indpendence assumptions for least squares fitting are not satisfied. However, this method can often give a reasonable fit. It can also sometimes be used to provide better starting values for the maximum likelihood fit.
Johnson, Kotz, and Balakrishnan (1994), "Continuous Univariate Distributions: Volume II", 2nd. ed., John Wiley and Sons. Johnson, Kotz, and Kemp (1994), "Univariate Discrete Distributions", 2nd. ed., John Wiley and Sons. Karl Bury (1999), "Statistical Distributions in Engineering", Cambridge University Press. Cohen and Whitten (1988), "Parameter Estimation in Reliability and Life Span Models", Marcel Dekker, p. 31 and pp. 341-344. Rinne (2009), "The Weibull Distribution: A Handbook", CRC Press. Castillo, Hadi, Balakrishnan, and Sarabia (2005), "Extreme Value and Related Models with Applications in Engineering and Science", Wiley. Lawless (2003), "Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data", Wiley, pp. 187-190. Evans, Hastings, and Peacock (2000), "Statistical Distributions", Third Edition, John Wiley and Sons.
New distributions have been continually added since the original implementation
skip 25
read vangel31.dat y
.
set write decimals 4
exponential mle y
weibull mle y
lognormal mle y
gamma mle y
The following output is generated.
2-Parameter Exponential Parameter Estimation
(without Bias Correction)
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 38
Sample Mean: 185.7895
Sample Standard Deviation: 18.5955
Sample Minimum: 147.0000
Sample Maximum: 231.0000
Maximum Likelihood:
Estimate of Location: 147.0000
Standard Error of Location: 1.0344
Estimate of Scale: 38.7894
Standard Error of Scale: 6.3769
Log-likelihood: -0.1770097E+03
AIC: 0.3580193E+03
AICc: 0.3583622E+03
BIC: 0.3612945E+03
Confidence Interval for Location Parameter
---------------------------------------------
Confidence Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------
50.00 145.5191 146.6972
75.00 144.7575 146.8598
90.00 143.7287 146.9462
95.00 142.9334 146.9733
99.00 141.0280 146.9946
99.90 138.1539 146.9995
---------------------------------------------
Confidence Interval for Scale Parameter
---------------------------------------------
Confidence Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------
50.00 36.0379 45.0266
75.00 33.4427 48.9044
90.00 31.0049 53.4162
95.00 29.5750 56.5803
99.00 27.0274 63.5112
99.90 24.4297 73.0144
---------------------------------------------
Two-Parameter Weibull (Minimum) Parameter Estimation:
Full Sample Case
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 38
Sample Mean: 185.7895
Sample Standard Deviation: 18.5955
Sample Minimum: 147.0000
Sample Maximum: 231.0000
Maximum Likelihood:
Estimate of Scale: 194.2045
Estimate of Shape (Gamma): 10.5731
Standard Error of Scale: 3.1373
Standard Error of Shape: 1.3372
Shape/Scale Covariance: 1.1460
Log-likelihood: -0.1664930E+03
AIC: 0.3369861E+03
AICc: 0.3373289E+03
BIC: 0.3402612E+03
Maximum Likelihood (Bias Corrected):
Estimate of Scale: 194.2045
Estimate of Shape (Gamma): 10.2050
Standard Error of Scale: 3.1373
Standard Error of Shape: 1.2458
Shape/Scale Covariance: 1.1460
Log-likelihood: -0.1665415E+03
AIC: 0.3370830E+03
AICc: 0.3374258E+03
BIC: 0.3403581E+03
Confidence Interval for Scale Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Normal Approximation Likelihood Ratio Approximation
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 192.0885 196.3206 192.0630 196.3353
75.00 190.5954 197.8136 190.5286 197.8516
90.00 189.0440 199.3650 188.9007 199.4568
95.00 188.0554 200.3536 187.8404 200.5043
99.00 186.1233 202.2857 185.7038 202.6331
99.90 183.8811 204.5280 183.0903 205.3014
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Confidence Interval for Shape Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Normal Approximation Likelihood Ratio Approximation
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 9.6712 11.4751 9.7392 11.4358
75.00 9.0348 12.1115 9.1684 12.0611
90.00 8.3734 12.7728 8.5913 12.7256
95.00 7.9520 13.1943 8.2321 13.1567
99.00 7.1284 14.0180 7.5498 14.0161
99.90 6.1726 14.9738 6.7919 15.0417
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Two-Parameter Lognormal Parameter Estimation:
Full Sample Case
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 38
Sample Mean: 185.7895
Sample Standard Deviation: 18.5955
Sample Minimum: 147.0000
Sample Maximum: 231.0000
Sample Median: 185.5000
Maximum Likelihood:
Estimate of Shape (Sigma): 0.1003
Standard Error of Shape: 0.0117
Estimate of Scale: 184.8847
Standard Error of Scale: 3.0314
Estimate of MU (= LOG(Scale)): 5.2196
Standard Error of MU: 0.0162
Log-likelihood: -0.1643679E+03
AIC: 0.3327358E+03
AICc: 0.3330786E+03
BIC: 0.3360109E+03
Confidence Interval for Scale Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Scale Parameter MU Parameter
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 182.8478 186.9442 5.2087 5.2308
75.00 181.4037 188.4324 5.2007 5.2386
90.00 179.8807 190.0278 5.1923 5.2472
95.00 178.8915 191.0786 5.1867 5.2526
99.00 176.8975 193.2324 5.1756 5.2638
99.90 174.4455 195.9487 5.1615 5.2778
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Confidence Interval for Shape Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Confidence Limit Upper
Coefficient Lower Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 0.0937 0.1097
75.00 0.0889 0.1165
90.00 0.0844 0.1243
95.00 0.0817 0.1297
99.00 0.0769 0.1414
99.90 0.0719 0.1574
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Two-Parameter Gamma Parameter Estimation:
Full Sample Case
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 38
Sample Mean: 185.7895
Sample Standard Deviation: 18.5955
Sample Minimum: 147.0000
Sample Maximum: 231.0000
Sample Geometric Mean: 184.8847
Method of Moments:
Estimate of Shape (Gamma): 99.8221
Estimate of Scale: 1.8612
Maximum Likelihood:
Estimate of Shape (Gamma): 102.5883
Standard Error of Shape: 23.4971
Estimate of Scale: 1.8109
Standard Error of Scale: 0.4158
Shape/Scale Covariance: -9.7466
Confidence Interval for Scale Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Normal Approximation Likelihood Ratio Approximation
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 1.5306 2.0914 1.5571 2.1230
75.00 1.3327 2.2894 1.4061 2.3873
90.00 1.1271 2.4950 1.2695 2.7100
95.00 0.9960 2.6259 1.1916 2.9459
99.00 0.7399 2.8820 1.0570 3.4902
99.90 0.4428 3.1793 0.9257 4.2976
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Confidence Interval for Shape Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Normal Approximation Likelihood Ratio Approximation
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 86.7396 118.4368 87.5478 119.2668
75.00 75.5583 129.6183 77.8833 132.0490
90.00 63.9388 141.2377 68.6407 146.2472
95.00 56.5345 148.6419 63.1638 155.7909
99.00 42.0634 163.1132 53.3517 175.5810
99.90 25.2699 179.9065 43.3751 200.4731
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Program 2:
. Purpose: Example of fitting 2-parameter Weibull using
. maximum likelihood
.
. Step 1: Read the data
.
skip 25
read weibbury.dat y
skip 0
.
. Step 2: Maximum likelihood estimates
.
set write decimals 5
set maximum likelihood percentiles default
set distributional percentile two-sided
feedback off
capture screen on
capture wei2.out
weibull mle y
let ksloc = 0
let ksscale = alphaml
let gamma = gammaml
.
. Step 3: Goodness of fit via Anderson-Darling and by
. probability plot
.
set goodness of fit fully specified on
set anderson darling critical value simulation
weibull anderson darling goodness of fit y
end of capture
.
let pploc = ksloc
let ppscale = ksscale
.
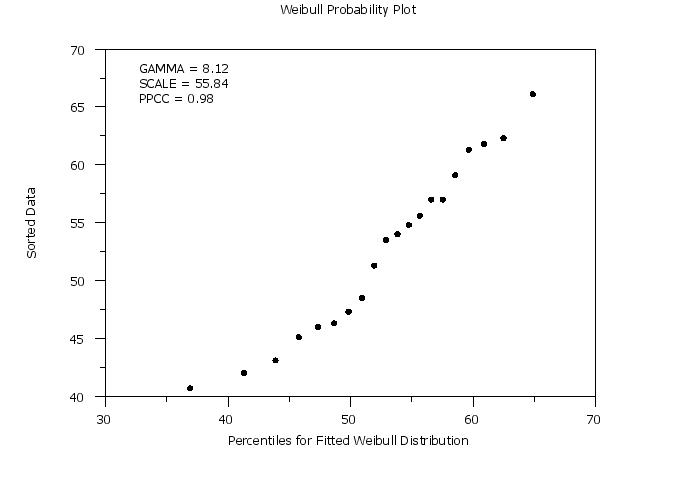
title case asis
label case asis
title Weibull Probability Plot
y1label Sorted Data
x1label Percentiles for Fitted Weibull Distribution
character circle
character hw 1 0.75
character fill on
line blank
.
weibull probability plot y
.
let gamma = round(gamma,2)
move 20 85
text Gamma = ^gamma
let ksscale = round(ksscale,2)
move 20 82
text Scale = ^ksscale
let ppcc = round(ppcc,3)
move 20 79
text PPCC = ^ppcc
The following output is generated.
Two-Parameter Weibull (Minimum) Parameter Estimation:
Full Sample Case
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 20
Sample Mean: 52.64000
Sample Standard Deviation: 7.48517
Sample Minimum: 40.70000
Sample Maximum: 66.09999
Maximum Likelihood:
Estimate of Scale: 55.83881
Estimate of Shape (Gamma): 8.11761
Standard Error of Scale: 1.61954
Standard Error of Shape: 1.41527
Shape/Scale Covariance: 0.84710
Log-likelihood: -0.6835433E+02
AIC: 0.1407087E+03
AICc: 0.1414145E+03
BIC: 0.1427001E+03
Maximum Likelihood (Bias Corrected):
Estimate of Scale: 55.83881
Estimate of Shape (Gamma): 7.55464
Standard Error of Scale: 1.61954
Standard Error of Shape: 1.22578
Shape/Scale Covariance: 0.84710
Log-likelihood: -0.6844503E+02
AIC: 0.1408901E+03
AICc: 0.1415959E+03
BIC: 0.1428815E+03
Confidence Interval for Scale Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Normal Approximation Likelihood Ratio Approximation
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 54.74645 56.93119 54.73232 56.93923
75.00 53.97578 57.70186 53.92918 57.73490
90.00 53.17490 58.50274 53.06172 58.60202
95.00 52.66458 59.01306 52.48611 59.18824
99.00 51.66716 60.01048 51.29590 60.44785
99.90 50.50966 61.16798 49.77662 62.19297
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Confidence Interval for Shape Parameter
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Normal Approximation Likelihood Ratio Approximation
Confidence Lower Upper Lower Upper
Coefficient Limit Limit Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
50.00 7.16302 9.07219 7.19360 9.10074
75.00 6.48955 9.74566 6.57700 9.83032
90.00 5.78969 10.44552 5.96703 10.62030
95.00 5.34372 10.89148 5.59468 11.14076
99.00 4.47210 11.76310 4.90364 12.19666
99.90 3.46061 12.77459 4.16282 13.48682
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Confidence Intervals for Select Percentiles (alpha = 0.050)
(Based on Normal Approximation)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Point Standard Lower Upper
Percentile Estimate Error Limit Limit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
0.500 29.08095 3.66048 21.90653 36.25536
1.000 31.68303 3.52762 24.76901 38.59707
5.000 38.72843 3.01713 32.81494 44.64191
10.000 42.31954 2.69485 37.03772 47.60134
20.000 46.41828 2.30418 41.90216 50.93437
30.000 49.17916 2.04763 45.16586 53.19248
40.000 51.40420 1.86149 47.75574 55.05266
50.000 53.37375 1.72632 49.99020 56.75730
60.000 55.24069 1.63762 52.03099 58.45040
70.000 57.13040 1.60039 53.99371 60.26711
80.000 59.21016 1.63240 56.01073 62.40959
90.000 61.88098 1.79006 58.37254 65.38943
95.000 63.91991 1.98932 60.02091 67.81892
97.500 65.58001 2.19282 61.28213 69.87788
99.000 67.39704 2.44995 62.59519 72.19889
99.500 68.57125 2.63203 63.41255 73.72996
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anderson-Darling Goodness of Fit Test
(Fully Specified Model)
Response Variable: Y
H0: The distribution fits the data
Ha: The distribution does not fit the data
Distribution: WEIBULL
Location Parameter: 0.00000
Scale Parameter: 55.83881
Shape Parameter 1: 8.11761
Summary Statistics:
Number of Observations: 20
Sample Minimum: 40.70000
Sample Maximum: 66.09999
Sample Mean: 52.64000
Sample SD: 7.48517
Anderson-Darling Test Statistic Value: 0.29226
Number of Monte Carlo Simulations: 10000.00000
CDF Value: 0.05700
P-Value 0.94300
Percent Points of the Reference Distribution
-----------------------------------
Percent Point Value
-----------------------------------
0.0 = 0.000
50.0 = 0.774
75.0 = 1.237
90.0 = 1.927
95.0 = 2.513
97.5 = 3.033
99.0 = 3.758
99.5 = 4.357
Conclusions (Upper 1-Tailed Test)
----------------------------------------------
Alpha CDF Critical Value Conclusion
----------------------------------------------
10% 90% 1.927 Accept H0
5% 95% 2.513 Accept H0
2.5% 97.5% 3.033 Accept H0
1% 99% 3.758 Accept H0
Date created: 12/17/2014 |
Last updated: 12/11/2023 Please email comments on this WWW page to [email protected]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||