

|
CLUSTERName:
NORMAL MIXTURE CLUSTER K MEDOIDS CLUSTER FUZZY CLUSTER AGNES CLUSTER DIANA CLUSTER
The traditional clustering methods described above are heuristic methods and are intented for small to moderate size data sets. These methods tend to work reasonably well for spherical shaped or convex clusters. If clusters are not compact and well separated, these methods may not be effective. The k-means algorithm is sensitive to noise and outliers (the k-medoids method may work better in these cases). Dataplot does not currently support model-based clustering or some of the newer cluster methods such as DBSCAN that can work better for non-spherical shapes in the presence of significant noise.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y1> ... <yk> is a list of response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax performs Hartigan's k-means clustering.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y1> ... <yk> is a list of response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax performs Hartigan's normal mixture clustering.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y1> ... <yk> is a list of response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax performs Kaufman and Rousseeuw k-medoids clustering. The use of PAM or CLARA will be determined based on the number of objects to be clustered.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y1> ... <yk> is a list of response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax performs Kaufman and Rousseeuw fuzzy clustering using the FANNY algorithm.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y1> ... <yk> is a list of response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax performs Kaufman and Rousseeuw agglomerative nesting clustering using the AGNES algorithm. By default, this algoritm uses the average distance linking critierion. However, it can also be used for single linkage (nearest neighbor), complete linkage, Ward's method, the centroid method, and Gower's method. See above for details.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y1> ... <yk> is a list of response variables; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. This syntax performs Kaufman and Rousseeuw divisive clustering using the DIANA algorithm.
K MEANS CLUSTERING Y1 TO Y6 K MEDOIDS CLUSTERING Y1 TO Y6 AGNES CLUSTERING M
The desirability of standardization will depend on the specific data set. Kaufman and Rousseeuw (pp. 8-11) discuss some of the issues in deciding whether or not to standardize. By default, Dataplot will standardize the variables. The following commands can be used to specify whether or not you want the variables to be standardized
SET NORMAL MIXTURE SCALE <ON/OFF> SET K MEDOIDS SCALE <ON/OFF> SET FANNY SCALE <ON/OFF> SET AGNES SCALE <ON/OFF> The SET AGNES SCALE command also applies to the DIANA CLUSTER command. If you choose to standardize, the basic formula is
where loc and scale denote the desired location and scale parameters. To specify the location statistic, enter
where <stat> is one of: MEAN, MEDIAN, MIDMEAN. HARMONIC MEAN, GEOMETRIC MEAN, BIWEIGHT LOCATION, H10, H12, H15, H17, or H20. To specify the scale statistic, enter
where <stat> is one of: STANDARD DEVIATION, H10, H12, H15, H17, H20, BIWEIGHT SCALE, MEDIAN ABSOLUTE DEVIATION, SCALED MEDIAN ABSOLUTE DEVIATION, AVERAGE ABSOLUTE DEVIATION, INTERQUARTILE RANGE, NORMALIZED INTERQUARTILE RANGE, SN SCALE, or RANGE. The default is to use the mean for the location statistic and the standard deviation for the scale statistic. Rousseeuw recommends using the mean for the location statistic and the average absolute deviation for the scale statistic.
The COSINE DISTANCE can be replaced with a number of other distance measures.
K MEDOIDS is a synonym for K MEDOIDS CLUSTER FANNY is a synonym for FANNY CLUSTER AGNES is a synonym for AGNES CLUSTER DIANA is a synonym for DIANA CLUSTER
Hartigan (1975), "Clustering Algorithms", Wiley. Kaufman and Rousseeuw (1990), "Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction To Cluster Analysis", Wiley. Rousseeuw (1987), "Silhouettes: A Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis", Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, North Holland, Vol. 20, pp. 53-65. Kruskal and Landwehr (1983), "Icicle Plots: Better Displays for Hierarchial Clustering", The American Statistician, Vol. 37, No. 2, pp. 168.
2017/11: Changed the default for standardization to be ON rather than OFF. Fixed a bug where the k-means method always performed standardization. For k-means, the cluster centers written to dpst3f.dat were modified to write the unstandardized values rather than the standardized values.
case asis
label case asis
title case asis
title offset 2
.
. Step 1: Read the data
.
dimension 100 columns
skip 25
read iris.dat y1 y2 y3 y4 x
skip 0
set write decimals 3
.
. Step 2: Perform the k-means cluster analysis with 3 clusters
.
set random number generator fibbonacci congruential
seed 45617
let ncluster = 3
set k means initial distance
set k means silhouette on
feedback off
k-means y1 y2 y3 y4
The following output is generated
Summary of K-Means Cluster Analysis
---------------------------------------------
Number Within
of Points Cluster
Cluster in Cluster Sum of Squares
---------------------------------------------
1 53 64.496
2 49 39.774
3 48 53.736
read dpst4f.dat clustid si
.
. Step 3: Scatter plot matrix with clusters identified
.
line blank all
char 1 2 3
char color blue red green
frame corner coordinates 5 5 95 95
multiplot scale factor 4
tic offset units screen
tic offset 5 5
.
set scatter plot matrix tag on
scatter plot matrix y1 y2 y3 y4 clustid
.
justification center
move 50 97
text K-Means Clusters for IRIS.DAT
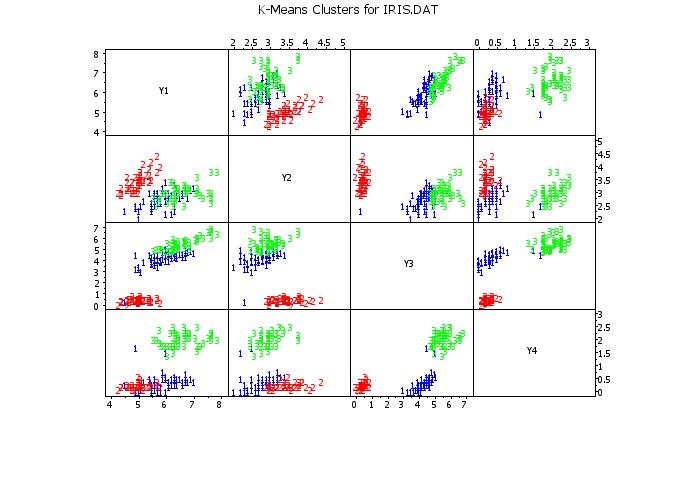
.
. Step 4: Silhouette Plot
.
. For better resolution, show the results for
. each cluster separately
.
let ntemp = size clustid
let indx = sequence 1 1 ntemp
let clustid = sortc clustid si indx
let x = sequence 1 1 ntemp
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let string t^k = ^itemp
end of loop
.
orientation portrait
device 2 color on
frame corner coordinates 15 20 85 90
tic offset units data
horizontal switch on
.
spike on
char blank all
line blank all
.
label size 1.7
xlimits 0 1
xtic mark offset 0 0
x1label S(i)
x1tic mark label size 1.7
y1tic mark offset 0.8 0.8
minor y1tic mark number 0
y1tic mark label format group label
y1tic mark label size 1.2
y1tic mark size 0.8
y1label Sequence Number
.
let simean = mean si
let simean = round(simean,2)
x3label Mean of All s(i) values: ^simean
.
loop for k = 1 1 ncluster
let sit = si
let xt = x
retain sit xt subset clustid = k
let ntemp2 = size sit
let y1min = minimum xt
let y1max = maximum xt
y1limits y1min y1max
major y1tic mark number ntemp2
let ig = group label t^y1min to t^y1max
y1tic mark label content ig
title Silhouette Plot for Cluster ^k Based on K-Means Clustering
.
let simean^k = mean si subset clustid = k
let simean^k = round(simean^k,2)
x2label Mean of s(i) values for cluster ^k: ^simean^k
.
plot si x subset clustid = k
end of loop
.
label
ylimits
major y1tic mark number
minor y1tic mark number
y1tic mark label format numeric
y1tic mark label content
y1tic mark label size
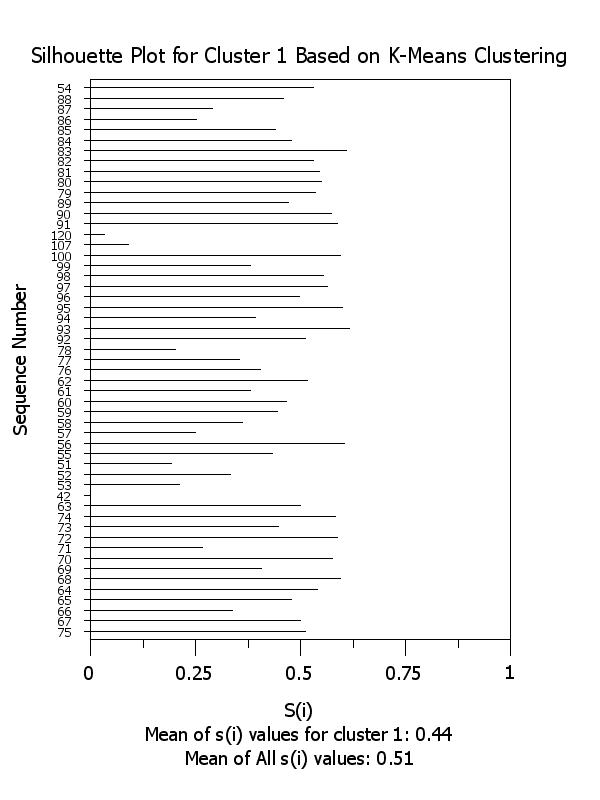
.
. Step 5: Display clusters in terms of first 2 principal components
.
orientation landscape
.
let ym = create matrix y1 y2 y3 y4
let pc = principal components ym
read dpst1f.dat clustid
spike blank all
character 1 2 3
character color red blue green
horizontal switch off
tic mark offset 0 0
limits
title Clusters for First Two Principal Components
y1label First Principal Component
x1label Second Principal Component
x2label
.
plot pc1 pc2 clustid
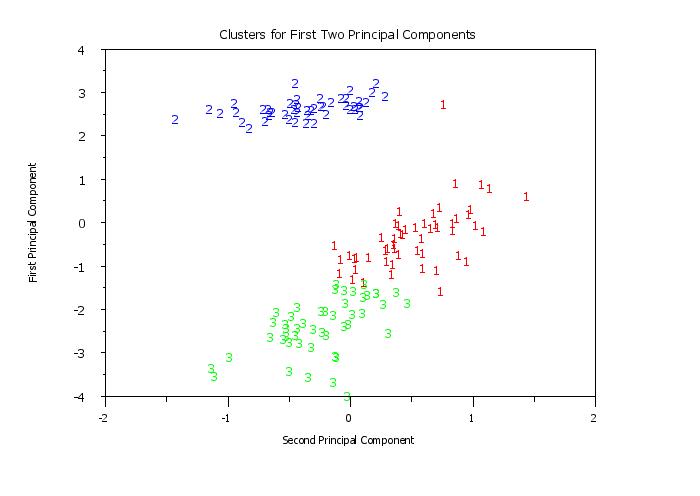 Program 2:
Program 2:
case asis
label case asis
title case asis
title offset 2
.
. Step 1: Read the data
.
dimension 100 columns
skip 25
read iris.dat y1 y2 y3 y4 x
skip 0
set write decimals 3
.
. Step 2: Perform the k-medoids cluster analysis with 3 clusters
.
set random number generator fibbonacci congruential
seed 45617
let ncluster = 3
set k medoids cluster distance manhattan
k medoids y1 y2 y3 y4
The following output is generated
**********************************************
* *
* ROUSSEEUW/KAUFFMAN K-MEDOID CLUSTERING *
* (USING THE CLARA ROUTINE). *
* *
**********************************************
**********************************************
* *
* NUMBER OF REPRESENTATIVE OBJECTS 3 *
* *
**********************************************
5 SAMPLES OF 46 OBJECTS WILL NOW BE DRAWN.
SAMPLE NUMBER 1
******************
RANDOM SAMPLE =
2 4 8 9 14 16 19 23 26 27
30 32 37 38 39 40 43 44 45 46
49 50 52 53 54 57 62 64 72 87
89 94 97 102 104 106 109 117 127 130
135 141 142 143 147 148
RESULT OF BUILD FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.00870
FINAL RESULT FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 0.978
RESULTS FOR THE ENTIRE DATA SET
TOTAL DISTANCE = 174.900
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.166
CLUSTER SIZE MEDOID COORDINATES OF MEDOID
1 50 8 5.00 3.40 0.50 0.20
2 51 62 5.90 3.00 4.20 0.50
3 49 117 6.50 3.00 5.50 1.80
AVERAGE DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
0.75 1.34
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
1.90 3.10
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO A MEDOID DIVIDED BY MINIMUM
DISTANCE OF THE MEDOID TO ANOTHER MEDOID
0.36 0.97
SAMPLE NUMBER 2
******************
RANDOM SAMPLE =
2 8 20 22 24 27 30 32 34 35
36 37 39 40 43 49 50 52 56 61
62 63 65 66 71 72 73 74 83 86
95 97 98 101 117 118 121 126 132 133
140 141 143 144 146 150
RESULT OF BUILD FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 0.97174
FINAL RESULT FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 0.970
RESULTS FOR THE ENTIRE DATA SET
TOTAL DISTANCE = 181.100
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.207
CLUSTER SIZE MEDOID COORDINATES OF MEDOID
1 50 8 5.00 3.40 0.50 0.20
2 55 97 5.70 2.90 4.20 0.30
3 45 121 6.90 3.20 5.70 2.30
AVERAGE DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
0.75 1.38
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
1.90 3.00
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO A MEDOID DIVIDED BY MINIMUM
DISTANCE OF THE MEDOID TO ANOTHER MEDOID
0.38 0.60
SAMPLE NUMBER 3
******************
RANDOM SAMPLE =
8 12 13 15 22 23 24 25 26 27
32 33 35 39 40 43 44 46 47 49
52 58 59 62 63 67 72 75 80 86
97 99 100 110 113 115 117 119 123 125
137 139 143 145 148 149
RESULT OF BUILD FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.01522
FINAL RESULT FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.015
RESULTS FOR THE ENTIRE DATA SET
TOTAL DISTANCE = 171.100
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.141
CLUSTER SIZE MEDOID COORDINATES OF MEDOID
1 50 8 5.00 3.40 0.50 0.20
2 50 97 5.70 2.90 4.20 0.30
3 50 113 6.80 3.00 5.50 2.10
AVERAGE DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
0.75 1.25
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
1.90 2.90
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO A MEDOID DIVIDED BY MINIMUM
DISTANCE OF THE MEDOID TO ANOTHER MEDOID
0.38 0.67
SAMPLE NUMBER 4
******************
RANDOM SAMPLE =
4 5 6 8 11 12 15 20 23 26
37 40 42 43 45 47 53 56 61 63
68 72 73 90 93 97 103 104 105 108
113 117 120 122 126 127 129 130 134 135
138 140 143 144 149 150
RESULT OF BUILD FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.00435
FINAL RESULT FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 0.983
RESULTS FOR THE ENTIRE DATA SET
TOTAL DISTANCE = 177.100
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.181
CLUSTER SIZE MEDOID COORDINATES OF MEDOID
1 50 40 5.10 3.40 0.50 0.20
2 49 93 5.80 2.60 4.00 0.20
3 51 117 6.50 3.00 5.50 1.80
AVERAGE DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
0.76 1.34
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
2.00 3.00
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO A MEDOID DIVIDED BY MINIMUM
DISTANCE OF THE MEDOID TO ANOTHER MEDOID
0.40 0.71
SAMPLE NUMBER 5
******************
RANDOM SAMPLE =
8 12 16 17 18 23 24 26 29 41
44 48 49 51 52 54 55 56 57 59
62 66 67 71 73 77 79 81 97 100
101 102 106 108 111 113 114 117 118 120
121 123 127 134 137 146
RESULT OF BUILD FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.09130
FINAL RESULT FOR THIS SAMPLE
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.091
RESULTS FOR THE ENTIRE DATA SET
TOTAL DISTANCE = 172.800
AVERAGE DISTANCE = 1.152
CLUSTER SIZE MEDOID COORDINATES OF MEDOID
1 50 8 5.00 3.40 0.50 0.20
2 53 79 6.00 2.90 4.50 0.50
3 47 113 6.80 3.00 5.50 2.10
AVERAGE DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
0.75 1.33
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
1.90 3.40
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO A MEDOID DIVIDED BY MINIMUM
DISTANCE OF THE MEDOID TO ANOTHER MEDOID
0.33 0.97
FINAL RESULTS
*************
SAMPLE NUMBER 3 WAS SELECTED, WITH OBJECTS =
8 12 13 15 22 23 24 25 26 27
32 33 35 39 40 43 44 46 47 49
52 58 59 62 63 67 72 75 80 86
97 99 100 110 113 115 117 119 123 125
137 139 143 145 148 149
AVERAGE DISTANCE FOR THE ENTIRE DATA SET = 1.141
CLUSTERING VECTOR
*****************
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
3 3 3 3 3 3 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
CLUSTER SIZE MEDOID OBJECTS
1 50 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
2 50 97
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
71 72 73 74 75 76 77 79 80 81
82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91
92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 107
3 50 113
78 101 102 103 104 105 106 108 109 110
111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120
121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130
131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140
141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150
AVERAGE DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
0.750 1.248 1.424
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO EACH MEDOID
1.900 2.900 3.000
MAXIMUM DISTANCE TO A MEDOID DIVIDED BY MINIMUM
0.380 0.674 0.698
skip 1
read dpst4f.dat clustid si
skip 0
.
. Step 3: Scatter plot matrix with clusters identified
.
line blank all
char 1 2 3
char color blue red green
frame corner coordinates 5 5 95 95
multiplot scale factor 4
tic offset units screen
tic offset 5 5
.
set scatter plot matrix tag on
scatter plot matrix y1 y2 y3 y4 clustid
.
justification center
move 50 97
text K Medoids Clusters for IRIS.DAT
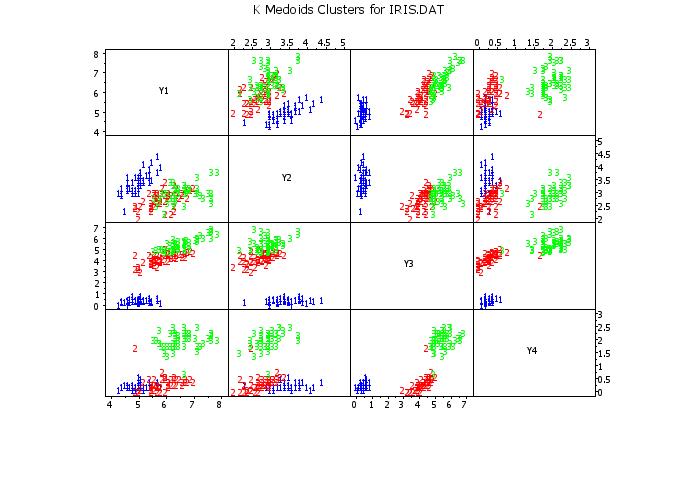
.
. Step 4: Silhouette Plot
.
. For better resolution, show the results for
. each cluster separately
.
let ntemp = size clustid
let indx = sequence 1 1 ntemp
let clustid = sortc clustid si indx
let x = sequence 1 1 ntemp
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let string t^k = ^itemp
end of loop
.
orientation portrait
device 2 color on
frame corner coordinates 15 20 85 90
tic offset units data
horizontal switch on
.
spike on
char blank all
line blank all
.
label size 1.7
xlimits 0 1
xtic mark offset 0 0
x1label S(i)
x1tic mark label size 1.7
y1tic mark offset 0.8 0.8
minor y1tic mark number 0
y1tic mark label format group label
y1tic mark label size 1.2
y1tic mark size 0.8
y1label Sequence Number
.
let simean = mean si
let simean = round(simean,2)
x3label Mean of All s(i) values: ^simean
.
orientation portait
device 2 color on
loop for k = 1 1 ncluster
.
.
let sit = si
let xt = x
retain sit xt subset clustid = k
let ntemp2 = size sit
let y1min = minimum xt
let y1max = maximum xt
y1limits y1min y1max
major y1tic mark number ntemp2
let ig = group label t^y1min to t^y1max
y1tic mark label content ig
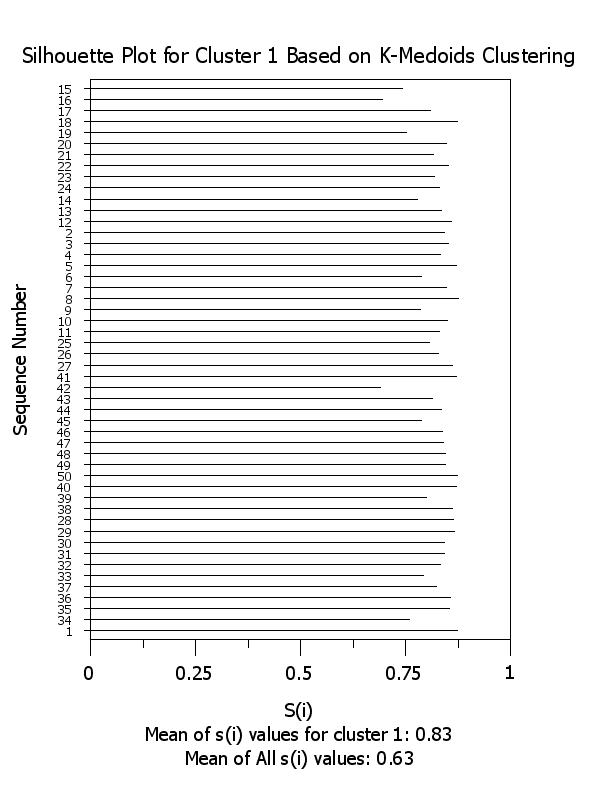
title Silhouette Plot for Cluster ^k Based on K-Medoids Clustering
.
let simean^k = mean si subset clustid = k
let simean^k = round(simean^k,2)
x2label Mean of s(i) values for cluster ^k: ^simean^k
.
plot si x subset clustid = k
end of loop
.
label
ylimits
major y1tic mark number
minor y1tic mark number
y1tic mark label format numeric
y1tic mark label content
y1tic mark label size
.
. Step 5: Display clusters in terms of first 2 principal components
.
orientation landscape
device 2 color on
.
let ym = create matrix y1 y2 y3 y4
let pc = principal components ym
read dpst1f.dat clustid
spike blank all
character 1 2 3
character color red blue green
horizontal switch off
tic mark offset 0 0
limits
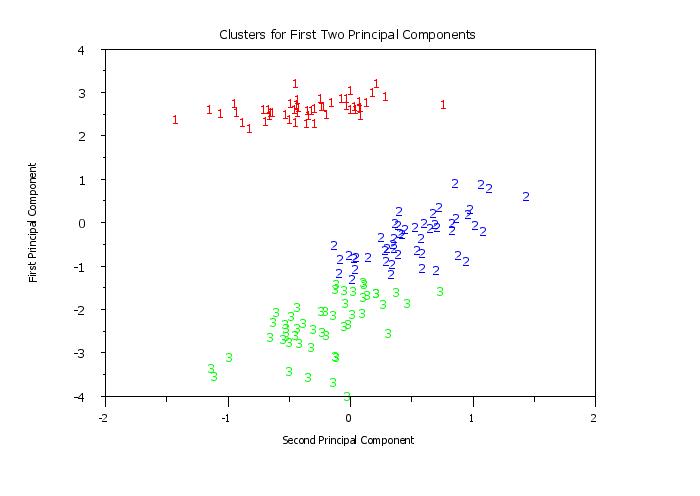
title Clusters for First Two Principal Components
y1label First Principal Component
x1label Second Principal Component
x2label
.
plot pc1 pc2 clustid
 Program 3:
Program 3:
orientation portait
.
case asis
label case asis
title case asis
title offset 2
.
. Step 1: Read the data
.
set write decimals 3
dimension 100 columns
.
skip 25
read matrix rouss1.dat y
skip 0
.
let string s1 = Belgium
let string s2 = Brazil
let string s3 = China
let string s4 = Cuba
let string s5 = Egypt
let string s6 = France
let string s7 = India
let string s8 = Israel
let string s9 = USA
let string s10 = USSR
let string s11 = Yugoslavia
let string s12 = Zaire
.
. Step 2: Perform the k-mediods cluster analysis with 3 clusters
.
let ncluster = 3
.
capture screen on
capture CLUST4A.OUT
k medioids y
end of capture
skip 1
read dpst4f.dat indx clustid si neighbor
skip 0
.
. Step 3: Silhouette Plot
.
. Create axis label
.
. First sort by cluster and then sort by
. silhouette within cluster (this second step
. is a bit convoluted)
.
let simean = mean si
let simean = round(simean,2)
.
let ntemp = size indx
let clustid = sortc clustid si indx neighbor
.
loop for k = 1 1 ncluster
.
let simean^k = mean si subset clustid = ^k
let simean^k = round(simean^k,2)
.
let clustidt = clustid
let sit = si
let indxt = indx
let neight = neighbor
retain clustidt sit indxt neight subset clustid = k
.
let sit = sortc sit clustidt indxt neight
if k = 1
let clustid2 = clustidt
let si2 = sit
let indx2 = indxt
let neigh2 = neight
else
let clustid2 = combine clustid2 clustidt
let si2 = combine si2 sit
let indx2 = combine indx2 indxt
let neigh2 = combine neigh2 neight
end of if
end of loop
let clustid = clustid2
let si = si2
let indx = indx2
let neighbor = neigh2
.
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let string t^k = ^s^itemp
end of loop
let ig = group label t1 to t^ntemp
.
let x = sequence 1 1 ntemp
.
frame corner coordinates 15 20 85 90
tic offset units data
horizontal switch on
.
spike on all
spike color red blue green
char blank all
line blank all
.
xlimits 0 1
xtic mark offset 0 0
major xtic mark number 6
x1tic mark decimal 1
y1limits 1 ntemp
y1tic mark offset 1 1
major y1tic mark number ntemp
minor y1tic mark number 0
y1tic mark label format group label
y1tic mark label content ig
y1tic mark label size 1.1
y1tic mark size 0.1
x1label S(i)
x3label Mean of All s(i) values: ^simean
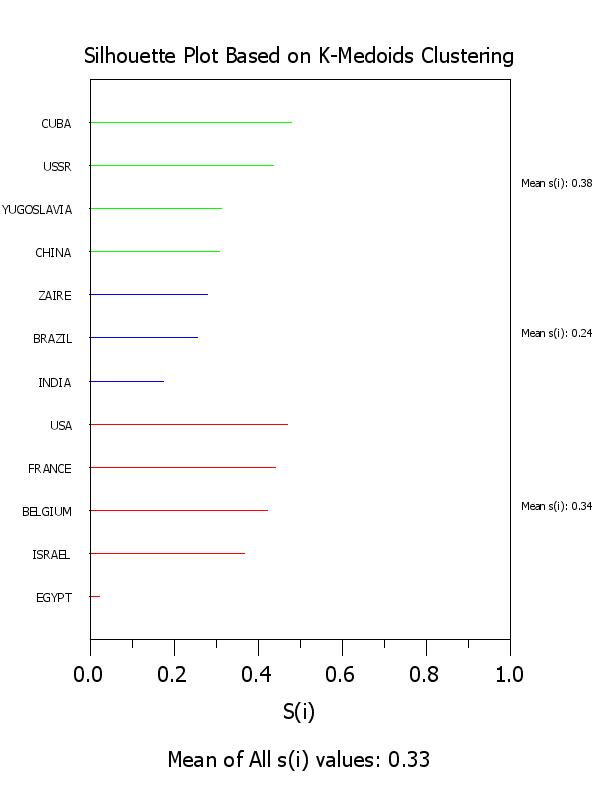
title Silhouette Plot Based on K-Medoids Clustering
.
plot si x clustid
.
height 1.0
justification left
movesd 87 3
text Mean s(i): ^simean1
movesd 87 7
text Mean s(i): ^simean2
movesd 87 10.5
text Mean s(i): ^simean3
height 2
.
print indx clustid neighbor si
The following output is generated
**********************************************
* *
* ROUSSEEUW/KAUFFMAN K-MEDOID CLUSTERING *
* (USING THE PAM ROUTINE). *
* *
**********************************************
DISSIMILARITY MATRIX
--------------------
1
2 5.58
3 7.00 6.50
4 7.08 7.00 3.83
5 4.83 5.08 8.17 5.83
6 2.17 5.75 6.67 6.92 4.92
7 6.42 5.00 5.58 6.00 4.67 6.42
8 3.42 5.50 6.42 6.42 5.00 3.92 6.17
9 2.50 4.92 6.25 7.33 4.50 2.25 6.33 2.75
10 6.08 6.67 4.25 2.67 6.00 6.17 6.17 6.92
6.17
11 5.25 6.83 4.50 3.75 5.75 5.42 6.08 5.83
6.67 3.67
12 4.75 3.00 6.08 6.67 5.00 5.58 4.83 6.17
5.67 6.50 6.92
**********************************************
* *
* NUMBER OF REPRESENTATIVE OBJECTS 3 *
* *
**********************************************
RESULT OF BUILD
AVERAGE DISSIMILARITY = 2.58333
FINAL RESULTS
AVERAGE DISSIMILARITY = 2.507
CLUSTERS
NUMBER MEDOID SIZE OBJECTS
1 9 5 1 5 6 8 9
2 12 3 2 7 12
3 4 4 3 4 10 11
CLUSTERING VECTOR
*****************
1 2 3 3 1 1 2 1 1 3 3 2
CLUSTERING CHARACTERISTICS
**************************
CLUSTER 3 IS ISOLATED
WITH DIAMETER = 4.50 AND SEPARATION = 5.25
THEREFORE IT IS AN L*-CLUSTER.
THE NUMBER OF ISOLATED CLUSTERS = 1
DIAMETER OF EACH CLUSTER
5.00 5.00 4.50
SEPARATION OF EACH CLUSTER
5.00 4.50 5.25
AVERAGE DISSIMILARITY TO EACH MEDOID
2.40 2.61 2.56
MAXIMUM DISSIMILARITY TO EACH MEDOID
4.50 4.83 3.83
------------------------------------------------------------
INDX CLUSTID NEIGHBOR SI
------------------------------------------------------------
5.000 1.000 2.000 0.021
8.000 1.000 2.000 0.366
1.000 1.000 2.000 0.421
6.000 1.000 2.000 0.440
9.000 1.000 2.000 0.468
7.000 2.000 3.000 0.175
2.000 2.000 1.000 0.255
12.000 2.000 1.000 0.280
3.000 3.000 2.000 0.307
11.000 3.000 1.000 0.313
10.000 3.000 1.000 0.437
4.000 3.000 2.000 0.479
 Program 4:
Program 4:
. Step 1: Read the data - a dissimilarity matrix
.
dimension 100 columns
set write decimals 3
.
skip 25
read matrix rouss1.dat y
skip 0
.
let string s1 = Belgium
let string s2 = Brazil
let string s3 = China
let string s4 = Cuba
let string s5 = Egypt
let string s6 = France
let string s7 = India
let string s8 = Israel
let string s9 = USA
let string s10 = USSR
let string s11 = Yugoslavia
let string s12 = Zaire
.
. Step 2: Perform the agnes cluster analysis
.
set agnes cluster banner plot on
agnes y
The following output is generated
**********************************************
* *
* ROUSSEEUW/KAUFFMAN AGGLOMERATIVE NESTING *
* CLUSTERING (USING THE AGNES ROUTINE). *
* *
* DATA IS A DISSIMILARITY MATRIX. *
* *
* USE AVERAGE LINKAGE METHOD. *
* *
**********************************************
DISSIMILARITY MATRIX
-------------------------
001
002 5.58
003 7.00 6.50
004 7.08 7.00 3.83
005 4.83 5.08 8.17 5.83
006 2.17 5.75 6.67 6.92 4.92
007 6.42 5.00 5.58 6.00 4.67 6.42
008 3.42 5.50 6.42 6.42 5.00 3.92 6.17
009 2.50 4.92 6.25 7.33 4.50 2.25 6.33 2.75
010 6.08 6.67 4.25 2.67 6.00 6.17 6.17 6.92
6.17
011 5.25 6.83 4.50 3.75 5.75 5.42 6.08 5.83
6.67 3.67
012 4.75 3.00 6.08 6.67 5.00 5.58 4.83 6.17
5.67 6.50 6.92
CLUSTER RESULTS
---------------
THE FINAL ORDERING OF THE OBJECTS IS
1 6 9 8 2
12 5 7 3 4
10 11
THE DISSIMILARITIES BETWEEN CLUSTERS ARE
2.170 2.375 3.363 5.532 3.000
4.978 4.670 6.417 4.193 2.670
3.710
************
* *
* BANNER *
* *
************
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 8 8 8 9 9 0
0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0
001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+0
*****************************************************
006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+0
***************************************************
009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009
***************************************
008+008+008+008+008+008+008+008+008+008
**************
002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002
*******************************************
012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012
********************
005+005+005+005+005+005+
************************
007+007+007+007+007+007+
***
003+003+003+003+003+003+003+0
*****************************
004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004
***********************************************
010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010
***********************************
011+011+011+011+011+011+011+011+011
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 8 8 8 9 9 0
0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0
THE ACTUAL HIGHEST LEVEL IS 6.4171875000
THE AGGLOMERATIVE COEFFICIENT OF THIS DATA SET IS 0.50
.
. Step 3: Generate dendogram from dpst3f.dat file
.
skip 0
read dpst1f.dat indx
read dpst3f.dat xd yd tag
.
orientation portrait
case asis
label case asis
title case asis
title offset 2
label size 1.5
tic mark label size 1.5
title size 1.5
tic mark offset units data
.
let ntemp = size indx
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let string t^k = ^s^itemp
end of loop
let ig = group label t1 to t^ntemp
.
x1label Distance
ylimits 1 12
major ytic mark number 12
minor ytic mark number 0
y1tic mark label format group label
y1tic mark label content ig
ytic mark offset 0.9 0.9
frame corner coordinates 15 20 95 90
.
pre-sort off
horizontal switch on
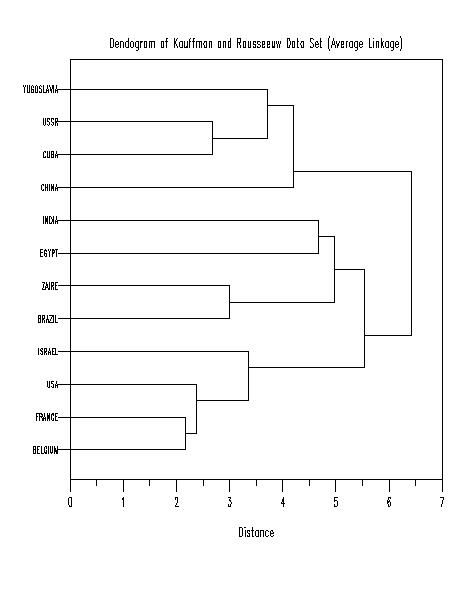
title Dendogram of Kauffman and Rousseeuw Data Set (Average Linkage)
plot yd xd tag
.
. Step 4: Generate icicle plot from dpst2f.dat file
.
delete xd yd tag
skip 0
read dpst1f.dat indx
read dpst2f.dat xd yd tag
.
set string space ignore
let ntemp = size indx
let ntic = 2*ntemp - 1
let string tcr = sp()cr()
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let ktemp1 = (k-1)*2 + 1
let ktemp2 = ktemp1 + 1
let string t^ktemp1 = ^s^itemp
if k < ntemp
let string t^ktemp2 = sp()
end of if
end of loop
let ig = group label t1 to t^ntic
.
ylimits 1 ntic
major ytic mark number ntic
minor ytic mark number 0
y1tic mark label format group label
y1tic mark label content ig
ytic mark offset 0.9 0.9
frame corner coordinates 15 20 95 90
.
xlimits 0 12
major x1tic mark number 13
minor x1tic mark number 0
.
line blank all
character blank all
bar on all
bar fill on all
bar fill color blue all
.
x1label Number of Clusters
title Icicle Plot of Kauffman and Rousseeuw Data Set (Average Linkage)
plot yd xd tag
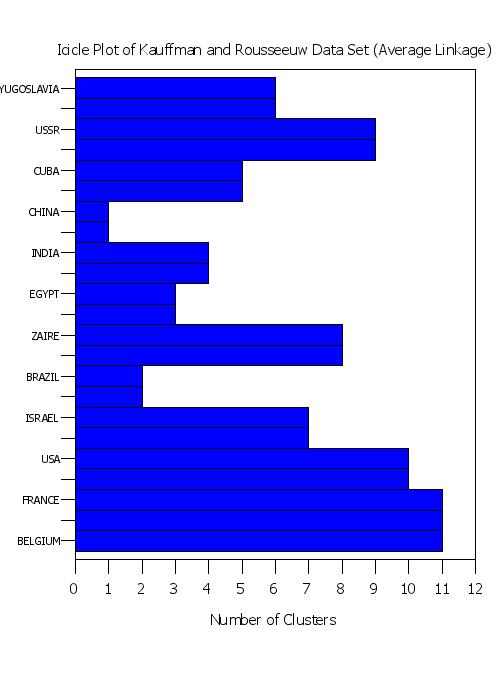 Program 5:
Program 5:
case asis
label case asis
title case asis
title offset 2
.
. Step 1: Read the data - a dissimilarity matrix
.
dimension 100 columns
set write decimals 3
.
skip 25
read matrix rouss1.dat y
skip 0
.
let string s1 = Belgium
let string s2 = Brazil
let string s3 = China
let string s4 = Cuba
let string s5 = Egypt
let string s6 = France
let string s7 = India
let string s8 = Israel
let string s9 = USA
let string s10 = USSR
let string s11 = Yugoslavia
let string s12 = Zaire
.
. Step 2: Perform the agnes cluster analysis
.
set agnes cluster banner plot on
set agnes cluster method average linkage
agnes y
The following output is generated
**********************************************
* *
* ROUSSEEUW/KAUFFMAN AGGLOMERATIVE NESTING *
* CLUSTERING (USING THE AGNES ROUTINE). *
* *
* DATA IS A DISSIMILARITY MATRIX. *
* *
* USE AVERAGE LINKAGE METHOD. *
* *
**********************************************
DISSIMILARITY MATRIX
-------------------------
001
002 5.58
003 7.00 6.50
004 7.08 7.00 3.83
005 4.83 5.08 8.17 5.83
006 2.17 5.75 6.67 6.92 4.92
007 6.42 5.00 5.58 6.00 4.67 6.42
008 3.42 5.50 6.42 6.42 5.00 3.92 6.17
009 2.50 4.92 6.25 7.33 4.50 2.25 6.33 2.75
010 6.08 6.67 4.25 2.67 6.00 6.17 6.17 6.92
6.17
011 5.25 6.83 4.50 3.75 5.75 5.42 6.08 5.83
6.67 3.67
012 4.75 3.00 6.08 6.67 5.00 5.58 4.83 6.17
5.67 6.50 6.92
CLUSTER RESULTS
---------------
THE FINAL ORDERING OF THE OBJECTS IS
1 6 9 8 2
12 5 7 3 4
10 11
THE DISSIMILARITIES BETWEEN CLUSTERS ARE
2.170 2.375 3.363 5.532 3.000
4.978 4.670 6.417 4.193 2.670
3.710
************
* *
* BANNER *
* *
************
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 8 8 8 9 9 0
0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0
001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+001+0
*****************************************************
006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+006+0
***************************************************
009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009+009
***************************************
008+008+008+008+008+008+008+008+008+008
**************
002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002+002
*******************************************
012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012+012
********************
005+005+005+005+005+005+
************************
007+007+007+007+007+007+
***
003+003+003+003+003+003+003+0
*****************************
004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004+004
***********************************************
010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010+010
***********************************
011+011+011+011+011+011+011+011+011
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 8 8 8 9 9 0
0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0 4 8 2 6 0
THE ACTUAL HIGHEST LEVEL IS 6.4171875000
THE AGGLOMERATIVE COEFFICIENT OF THIS DATA SET IS 0.50
.
. Step 3: Generate dendogram from dpst3f.dat file
.
skip 0
read dpst1f.dat indx
read dpst3f.dat xd yd tag
.
let ntemp = size indx
let string tcr = sp()cr()
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let string t^k = ^s^itemp
let ival1 = mod(k,2)
if ival1 = 0
let t^k = string concatenate tcr t^k
end of if
end of loop
let ig = group label t1 to t^ntemp
.
xlimits 1 12
major xtic mark number 12
minor xtic mark number 0
x1tic mark label format group label
x1tic mark label content ig
xtic mark offset 0.9 0.9
frame corner coordinates 15 20 95 90
.
y1label Distance
title Dendogram of Kauffman and Rousseeuw Data Set (Average Linkage)
plot yd xd tag
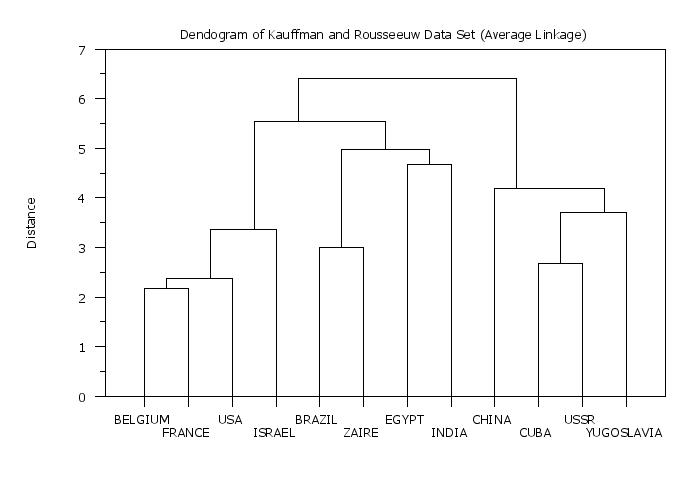
.
. Step 4: Generate icicle plot from dpst2f.dat file
.
delete xd yd tag
skip 0
read dpst1f.dat indx
read dpst2f.dat xd yd tag
.
set string space ignore
let ntemp = size indx
let ntic = 2*ntemp - 1
let string tcr = sp()cr()
loop for k = 1 1 ntemp
let itemp = indx(k)
let ktemp1 = (k-1)*2 + 1
let ktemp2 = ktemp1 + 1
let string t^ktemp1 = ^s^itemp
if k < ntemp
let string t^ktemp2 = sp()
end of if
let ival1 = mod(k,2)
if ival1 = 0
let t^ktemp1 = string concatenate tcr t^ktemp1
end of if
end of loop
let ig = group label t1 to t^ntic
.
xlimits 1 ntic
major xtic mark number ntic
minor xtic mark number 0
x1tic mark label format group label
x1tic mark label content ig
xtic mark offset 0.9 0.9
frame corner coordinates 15 20 95 90
.
ylimits 0 12
major y1tic mark number 13
minor y1tic mark number 0
.
line blank all
character blank all
bar on all
bar fill on all
bar fill color blue all
.
y1label Number of Clusters
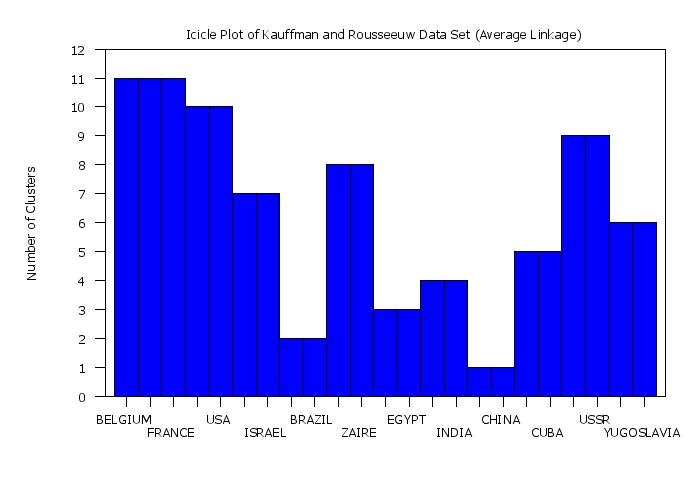
title Icicle Plot of Kauffman and Rousseeuw Data Set (Average Linkage)
plot yd xd tag
Date created: 09/26/2017 |
Last updated: 12/11/2023 Please email comments on this WWW page to [email protected]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||