CONVERT CHARACTER (SET)
Name:
Type:
Purpose:
Specifies how Dataplot will handle character data.
Description:
In versions of Dataplot prior to January, 2004, Dataplot did not
support reading character variables in data files. The one
execption was the READ ROW LABELS command (HELP READ ROW LABELS
for details). If encountered, Dataplot would generate an error
message and not read the data file correctly. To address
this, we have added the command
SET CONVERT CHARACTER <ON/CATEGORICAL/IGNORE/ERROR>
These options result in the following actions:
- Specifying ERROR continues the current Dataplot action of
reporting an error. This is recommended for the case
when a file is suppossed to contain only numeric data
and the presence of character data is in fact indicative
of an error in the data file.
To maintain compatibility with previous versions of
Dataplot, this is the default setting.
- Specifying IGNORE instructs Dataplot to simply ignore any
fields containing character data. No error or warning
messages are printed.
- Specifying ON instructs Dataplot to read character.
The character fields are written to the file
"dpzchf.dat" in the current directory.
The first line of this file specifies the number of
character fields. Lines 2 thru N+1 (with N denoting
the number of character fields) identify the names
of the character variables. Each of the remaining lines
contain the character fields for one row of character
data. Each character variable is written as 24
characters (character fields with more than 24 characters
are truncated and those with less than 24 characters
are right-padded with spaces) followed by one space.
As with numeric variables, character variable names can
be up to eight characters long. Note that Dataplot does
not save the character variable names in its internal
name table (they are only saved in the "dpchzf.dat"
file). Be aware that the "dpchzf.dat" file is overwritten
each time a file with character data is encoutered.
- This is similar to SET CONVERT CHARACTER ON. However, in
addition to creating the character variable, it will create
a numeric variable that converts the unique values of the
character field to an integer code. Currently, the code values
are assigned in the order that the unique values are detected
in the file. Up to 1,000 levels are supported (if more than
1,000 levels are required, the remaining levels are all set
to "-1").
Note that there will be both a numeric variable and a character
variable (in dpzchf.dat) with the same name. The context of
how the variable name is used determines whether the numeric or
character variable is being referred to (i.e., there are a
limited number of commands that specifically refer to the
character variables).
There are some restrictions on when Dataplot will try to
read character data:
- This only applies to the variable read case. That
is, READ PARAMETER and READ MATRIX will ignore
character fields or treat them as an error.
- Dataplot will only try to read character data from
a file. When reading from the keyboard (i.e., when
READ is specified with no file name), character data
will be ignored when a SET CONVERT CHARACTER ON is
specified.
- This capability is not supported for the SERIAL READ
case.
- The SET READ FORMAT command does not accept the
"A" format specification for reading character
fields.
Some of these restrictions may be addressed in subsequent
releases of Dataplot.
Syntax:
SET CONVERT CHARACTER <ON/CATEGORICAL/IGNORE/ERROR>
where <ON> specifies that character data will be read and
saved in dpchzf.dat, CATEGORICAL is similar to ON but
will also create a numeric categorical variable, IGNORE
specifies that character data will be ignored, and ERROR
specifies that character data will be treated as an error.
Examples:
SET CONVERT CHARACTER ON
SET CONVERT CHARACTER CATEGORICAL
SET CONVERT CHARACTER IGNORE
SET CONVERT CHARACTER ERROR
Note:
If the ON or CATEGORICAL options are used, you can specify one of
the variables to be the row label variable with the command
SET ROW LABEL COLUMN <ival>
where <ival> is an integer value that specifies which column of the
data is a row label variable. The values in this column are stored
in the internal row label variable. This is demonstrated in the
Program 2 example below. Although a row label variable is typically
the first column, this is not required.
Note:
In recognizing character data, Dataplot treats certain
characters as delimiters:
spaces (non-printing characters, such as tabs, are treated
as spaces)
commas
: or ;
%
/ or \
( or)
If Dataplot encounters one of these characters in a character
field, it treats it as the end of the character field (the
delimiter will not be part of the string.
If you have character data that will contain one or more of
these delimiters, then the character fields need to be
enclosed in quotes (either single or double quotes may
be used). If the character fields may contain quotes,
then use one type (i.e., single or double) as the delimiter
and the other type in the character field. At the current
time, Dataplot will not accomodate both types of quotes
in the character fields.
Note:
Dataplot supports a limited number of commands that can
utilize the character data saved in "dpchzf.dat". As of
the January, 2004 version, this includes
LET Y = CHARACTER CODE IX
LET Y = ALPHABETIC CHARACTER CODE IX
LET IG = GROUP LABELS IX
LET ROWLABEL = IX
The TIC MARK LABEL FORMAT and TIC MARK LABEL CONTENT commands
have been updated to use group labels for the tic mark labels.
For details, enter
HELP CHARACTER CODE
HELP ALPHABETIC CHARACTER CODE
HELP GROUP LABELS
HELP ROWLABEL
HELP TIC MARK LABEL FORMAT
HELP TIC MARK LABEL CONTENT
We anticipate additional use will be made of character data
in subsequent versions of Dataplot.
Default:
ERROR (character data will be treated as an error)
Synonyms:
Related Commands:
|
READ
|
=
|
Carries out a column-wise input of data.
|
|
CHARACTER CODE
|
=
|
Converts character data to a coded numeric variable.
|
|
GROUP LABEL
|
=
|
Converts character data to a group label variable.
|
|
ROWLABEL
|
=
|
Define row labels from character data.
|
Applications:
Implementation Date:
2004/01
2018/07: Support for CATEGORICAL option
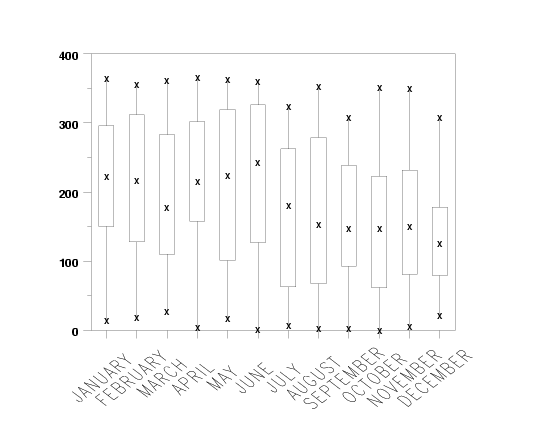
Program 1:
set convert character on
skip 25
read draft69c.dat rank day month
.
let ig = group label month
x1tic mark label format group label
x1tic mark label content ig
x1tic mark font simplex
x1tic mark angle 45
let xcode = character code month
.
major xtic mark number 12
minor xtic mark number 0
xlimits 1 12
xtic offset 0.5 0.5
.
char box plot
line box plot
fences on
.
box plot y xcode
Program 2:
SET CONVERT CHARACTER CATEGORICAL
SET ROW LABEL COLUMN 1
READ TEST_CHAR.DAT IROW Y X1 X2
.
SET WRITE DECIMALS 1
WRITE ROWLABEL Y X1 X2
The following output is returned
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ROWLABEL Y X1 X2
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Row_1 8.0 1.0 1.0
Row_2 2.0 2.0 2.0
Row_3 1.0 1.0 3.0
Row_4 7.0 2.0 1.0
Row_5 3.0 1.0 2.0
|
Privacy
Policy/Security Notice
Disclaimer |
FOIA
NIST is an agency of the U.S.
Commerce Department.
Date created: 2/3/2004
Last updated: 10/13/2015
Please email comments on this WWW page to
[email protected].
|
|


