2.
Measurement Process Characterization
2.3.
Calibration
2.3.6.
Instrument calibration over a regime
2.3.6.7.
Uncertainties of calibrated values
2.3.6.7.3.
|
Comparison of check standard analysis and propagation of error
|
|
|
Propagation of error for the linear calibration
|
The analysis of uncertainty for calibrated values from a linear
calibration line can be addressed using propagation of error. On
the previous page, the uncertainty was estimated
from check standard values.
|
|
Estimates from calibration data
|
The calibration data consist of 40 measurements with an optical
imaging system on 10 linewidth artifacts. A linear fit to the data
gives a
calibration curve with the following estimates for the intercept, \(a\),
and the slope, \(b\),
Parameter Estimate Std. Error t-value Pr(>|t|)
a 0.2357623 0.02430034 9.702014 7.860745e-12
b 0.9870377 0.00344058 286.881171 5.354121e-65
with the following covariance matrix.
a b
a 5.905067e-04 -7.649453e-05
b -7.649453e-05 1.183759e-05
The results shown above can be generated with
R code or
Dataplot code.
The reader can download the
data as a text file.
|
|
Propagation of error
|
The propagation of error is performed for the equation
$$ X' = \frac{Y'- \hat{a}}{\hat{b}} $$
so that the squared uncertainty of a calibrated value, \(X'\), is
$$ \hspace{-.25in}u^2 =
\left[ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{Y'}} \right]^2 s_{Y'}^2 \, + \,
\left[ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{\hat{a}}} \right]^2 s_{\hat{a}}^2 \, + \,
\left[ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{\hat{b}}} \right]^2 s_{\hat{b}}^2 \, + \,
2 \left[ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{\hat{a}}} \right]
\left[ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{\hat{b}}} \right] s_{\hat{a}\hat{b}} $$
where
$$ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{Y'}} = \frac{1}{\hat{b}} $$
$$ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{\hat{a}}} = \frac{-1}{\hat{b}} $$
$$ \frac{\partial{X'}}{\partial{\hat{b}}} = \frac{-(Y'-\hat{a})}{\hat{b}^{2}} $$
The uncertainty of the calibrated value, \(X'\),
$$ \hspace{-.25in}u^2 =
\left( \frac{1}{\hat{b}} \right)^2 s_{Y'}^2 \, + \,
\left( \frac{-1}{\hat{b}} \right)^2 s_{\hat{a}}^2 \, + \,
\left( \frac{-(Y'-\hat{a})}{\hat{b}^{2}} \right)^2 s_{\hat{b}}^2 \, + \,
2 \left( \frac{-1}{\hat{b}} \right)
\left( \frac{-(Y'-\hat{a})}{\hat{b}^{2}} \right) s_{\hat{a}\hat{b}} $$
is dependent on the value of the instrument reponse \(Y'\).
|
|
Graph showing standard deviation of calibrated value X' plotted as
a function of instrument response Y' for a linear calibration
|
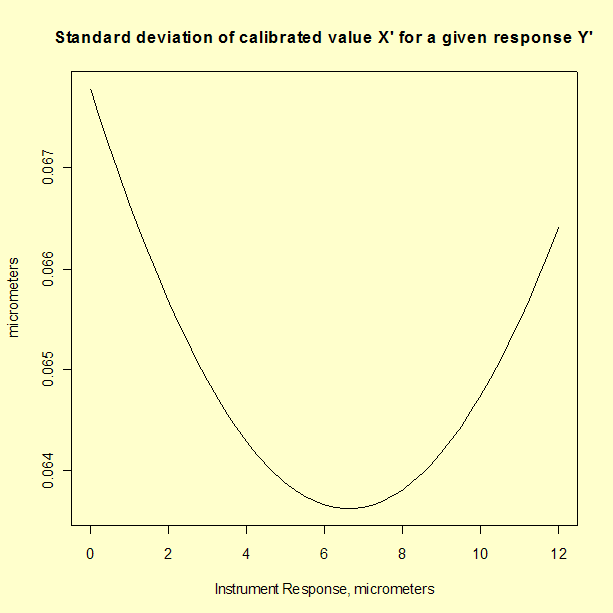
|
|
Comparison of check standard analysis and propagation of error
|
Comparison of the analysis of check standard
data, which gives a standard deviation of 0.119 μm, and
propagation of error, which gives a maximum standard deviation of
0.068 μm, suggests that the propagation of error may
underestimate the type A uncertainty. The check standard measurements
are undoubtedly sampling some sources of variability that do not appear
in the formal propagation of error formula.
|


