

|
SDEPPFName:
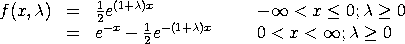
To compute the percent point function, Dataplot computes the cumulative distribution function for X = 0. If this value is PCUT and p is the input probability value, then
![G(p,lambda) = LOG[2*p*(1-lambda)]/(1+lambda)] p <= PCUT](eqns/sdeppf.gif)
If p is greater than PCUT, then Dataplot computes the percent point function by numerically inverting the cumulative distribution function.
For
The standard skew double exponential distribution can be
generalized with a location parameter,
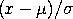
in the above formula for the probability density function. The skew double exponential distribution is also known as the skew Laplace distribution.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <p> is a variable, a number or a parameter in the interval (0,1); <lambda> is a number of parameter that specifies the value of the shape parameter; <loc> is an optional number or parameter that specifies the value of the location parameter; <scale> is an optional positive number or parameter that specifies the value of the scale parameter; <y> is a variable or a parameter (depending on what <x> is) where the computed skew double exponential ppf value is stored; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional.
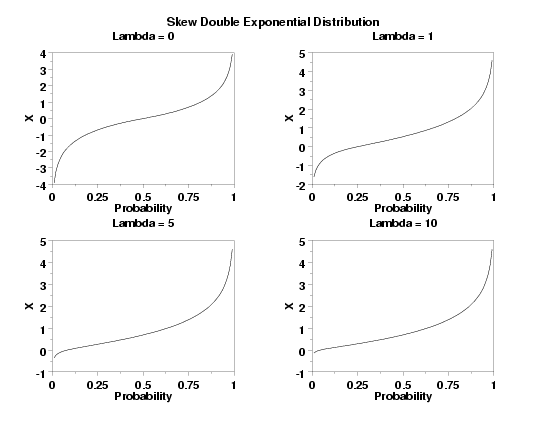
LET X = SDEPPF(P1,LAMBDA) PLOT SDEPPF(P,LAMBDA) FOR P = 0.01 0.01 0.99
"A Class of Distributions Which Includes the Normal Ones", Azzalini, Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 12, 171-178.
X1LABEL Probability
Y1LABEL X
LABEL CASE ASIS
TITLE CASE ASIS
CASE ASIS
X1LABEL DISPLACEMENT 12
MULTIPLOT 2 2
MULTIPLOT CORNER COORDINATES 0 0 100 95
MULTIPLOT SCALE FACTOR 2
TITLE Lambda = 0
PLOT SDEPPF(P,0) FOR P = 0.01 0.01 0.99
TITLE Lambda = 1
PLOT SDEPPF(P,1) FOR P = 0.01 0.01 0.99
TITLE Lambda = 5
PLOT SDEPPF(P,5) FOR P = 0.01 0.01 0.99
TITLE Lambda = 10
PLOT SDEPPF(P,10) FOR P = 0.01 0.01 0.99
END OF MULTIPLOT
MOVE 50 97
JUSTIFICATION CENTER
TEXT Skew Double Exponential Distribution
Date created: 7/7/2004 |