

|
RANK INDEXName:
The RANK INDEX command performs ranking. However, it handles ties differently. For example, if ranks 5 and 6 denote the same value, this command will return 5 and 6 as the ranks rather than 5.5 for both. This command is useful when you want to use the rank as an index to another variable. An example is given in the program example below.
where <x> is the variable for which the ranks are to be computed; <y> is a variable where the computed ranks are saved; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional.
skip 25
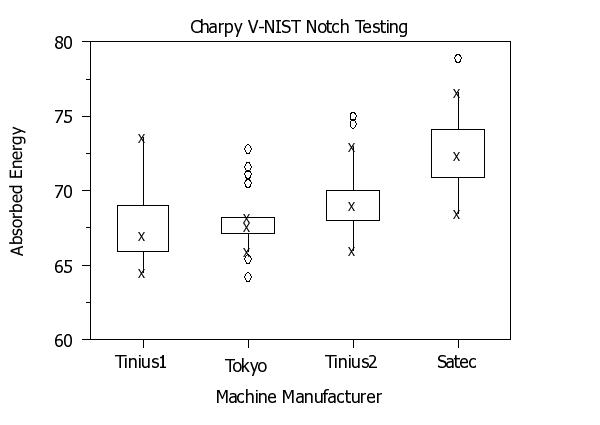
read splett2.dat y x
let string s1 = Tinius1
let string s2 = Tinius2
let string s3 = Satec
let string s4 = Tokyo
.
let xsort iindx = sort by median y x
set let cross tabulate collapse
let y2 = cross tabulate median y x
let x2 = rank index y2
loop for k = 1 1 4
let ival = x2(k)
let string t^ival = ^s^k
end of loop
x1tic mark label case asis
x1tic mark label format alpha
x1tic mark label content ^t1 ^t2 ^t3 ^t4
.
char box plot
line box plot
fences on
.
xlimits 1 4
major xtic mark number 4
minor xtic mark number 0
xtic offset 0.5 0.5
.
title case asis
title offset 2
title Charpy V-NIST Notch Testing
label case asis
x1label Machine Manufacturer
y1label Absorbed Energy
.
box plot y xsort
Date created: 9/8/2010 |