

|
LINEAR INTERCEPTName:
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <y> is dependent response variable; <x> is the independent response variable; <par> is a parameter where the linear intercept value is saved; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional.
LET A1 = LINEAR INTERCEPT Y X SUBSET X > 1
SKIP 25
READ BERGER1.DAT Y X
LET A = LINEAR INTERCEPT Y X
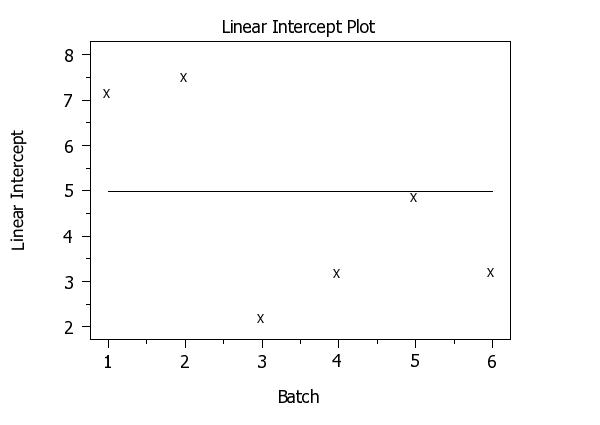
The result 4.9937 is returned.
Program 2:
SKIP 25
READ BERGER1.DAT Y X BATCH
.
LABEL CASE ASIS
TITLE CASE ASIS
Y1LABEL Linear Intercept
X1LABEL Batch
TITLE Linear Intercept Plot
CHARACTER X BLANK
LINE BLANK SOLID
TIC OFFSET UNITS SCREEN
TIC MARK OFFSET 3 3
LINEAR INTERCEPT PLOT Y X BATCH
|
Privacy
Policy/Security Notice
NIST is an agency of the U.S.
Commerce Department.
Date created: 09/08/2010 | ||||||||||||||