

|
IGPPFName:
![F(x;gamma,mu) = NORCDF[SQRT(gamma/x)*((x/mu) - 1)] +
EXP(2*gamma/mu)*NORCDF[-SQRT(gamma/x)*((x/mu) + 1)]
x >= 0; gamma, mu > 0](eqns/igcdf.gif)
with The percent point function is the inverse of the cumulative distribution function. The percent point function for the inverse Gaussian distribution does not exist in simple, closed form. It is computed by numerically inverting the inverse Gaussian cumulative distribution function using a bisection method. The inverse Gaussian distribution can be generalized with location and scale parameters in the usual way.
<SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> where <p> is a variable or a parameter in the interval (0,1); <gamma> is number or parameter that specifies the first shape parameter; <mu> is number or parameter that specifies the second shape parameter; <loc> is number or parameter that specifies the location parameter; <scale> is number or parameter that specifies the scale parameter; <y> is a variable or a parameter (depending on what <x> is) where the computed inverse Gaussian ppf value is stored; and where the <SUBSET/EXCEPT/FOR qualification> is optional. Note that the location and scale parameters are optional.
LET A = IGPPF(P1,2,1) PLOT IGPPF(P,2,1.5) FOR P = 0 0.01 0.99
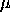 = 1 is
referred to as the Wald distribution. Enter HELP WALPDF for
details. = 1 is
referred to as the Wald distribution. Enter HELP WALPDF for
details.
"Statistical Distributions", Third Edition, Evans, Hastings, and Peacock, Wiley, 2000, pp. 114-116.
2003/12: Modified to treat 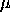 as a shape parameter instead of a location parameter.
as a shape parameter instead of a location parameter.
X1LABEL Probability
Y1LABEL X
LABEL CASE ASIS
X1LABEL DISPLACEMENT 12
Y1LABEL DISPLACEMENT 12
MULTIPLOT SCALE FACTOR 2
MULTIPLOT 2 2
MULTIPLOT CORNER COORDINATES 0 0 100 95
TITLE GAMMA = 2, MU = 1
PLOT IGPPF(P,2,1) FOR P = 0 0.01 0.99
TITLE GAMMA = 5, MU = 1
PLOT IGPPF(P,5,1) FOR P = 0 0.01 0.99
TITLE GAMMA = 2, MU = 2
PLOT IGPPF(P,2,2) FOR P = 0 0.01 0.99
TITLE GAMMA = 5, MU = 2
PLOT IGPPF(P,5,2) FOR P = 0 0.01 0.99
END OF MULTIPLOT
JUSTIFICATION CENTER
MOVE 50 97
CASE ASIS
TEXT Inverse Gaussian Percent Point
Date created: 7/7/2004 |