DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION HYPOTHESIS TEST
Name:
DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION HYPOTHESIS TEST (LET)
Type:
Purpose:
Return the p-value for a large sample hypothesis test for the
equality of two binomial proportions.
Description:
Given a set of N1 observations in a variable
X1 and a set of N2 observations
in a variable X2, we can compute a normal
approximation test that the two proportions are equal (or
alternatively, that the difference of the two proportions is
equal to 0). In the following, let p1 and
p2 be the population proportion of successes for
samples one and two, respectively.
The hypothesis test that the two binomial proportions are
equal is
|
H0:
|
p1 = p2
|
|
Ha:
|
p1 ≠ p2
|
|
Test Statistic:
|
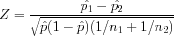
where  is the proportion of successes for the combined sample and
is the proportion of successes for the combined sample and
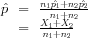
|
|
Significance Level:
|
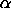
|
|
Critical Region:
|
For a two-tailed test
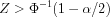
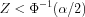
For a lower tailed test
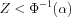
For an upper tailed test
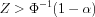
|
|
Conclusion:
|
Reject the null hypothesis if Z is in the critical
region
|
For a lower tailed test, the p-value is equal to NORCDF(Z).
For an upper tailed test, the p-value is equal to 1 - NORCDF(Z).
For a two-tailed test, the p-value is equal to 2*(1 - NORCDF(Z)).
Alternatively, you can request that the lower and upper confidence
limits for p1 - p2 be returned
instead of the p-value for the hypothesis test.
Syntax 1:
LET PVAL = DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION HYPOTHESIS TEST
<p1> <n1> <p2> <n2> <alpha>
where <p1> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 1;
<n1> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 1;
<p2> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 2;
<n2> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 2;
<alpha> is a parameter that specifies the desired
significance level;
and <pval> is the returned p-value.
This syntax is used for the two-tailed case.
Syntax 2:
LET PVAL = DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION LOWER TAIL HYPOTHESIS TEST
<p1> <n1> <p2> <n2> <alpha>
where <p1> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 1;
<n1> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 1;
<p2> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 2;
<n2> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 2;
<alpha> is a parameter that specifies the desired
significance level;
and <pval> is the returned p-value.
This syntax is used for the lower tailed case.
Syntax 3:
LET PVAL = DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION UPPER TAIL HYPOTHESIS TEST
<p1> <n1> <p2> <n2> <alpha>
where <p1> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 1;
<n1> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 1;
<p2> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 2;
<n2> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 2;
<alpha> is a parameter that specifies the desired
significance level;
and <pval> is the returned p-value.
This syntax is used for the upper tailed case.
Syntax 4:
LET <al> <au> = DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION CONFIDENCE LIMITS
<p1> <n1> <p2> <n2> <alpha>
where <p1> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 1;
<n1> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 1;
<p2> is a parameter that specifies the proportion of
successes for sample 2;
<n2> is a parameter that specifies the sample size for
sample 2;
<alpha> is a parameter that specifies the desired
significance level;
<al> is the returned lower confidence limit;
and <au> is the returned upper confidence limit.
This syntax is used for the two-tailed case.
Examples:
DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION HYPOTHESIS TEST Y1 Y2
DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION HYPOTHESIS TEST P1 N1 P2 N2
Note:
The BINOMIAL PROPORTION TEST generates this test with full
output.
Default:
Synonyms:
Related Commands:
References:
NIST/SEMATECH e-Handbook of Statistical Methods,
http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/prc/section3/prc33.htm.
Ryan (2008), "Modern Engineering Statistics", Wiley, pp. 124-126.
Applications:
Categorical Data Analysis
Implementation Date:
Program 1:
LET X1 = 32
LET N1 = 38
LET P1 = X1/N1
LET X2 = 39
LET N2 = 44
LET P2 = X1/N1
LET ALPHA = 0.05
LET PVAL = DIFFERENCE OF PROPORTION HYPOTHESIS TEST P1 N1 P2 N2

Date created: 1/26/2009
Last updated: 1/26/2009
Please email comments on this WWW page to
[email protected].
|

