6.4. Introduction to Time Series Analysis
6.4.5. Multivariate Time Series Models
6.4.5.1. |
Example of Multivariate Time Series Analysis |
In this experiment 296 successive pairs of observations \((x_t, \, y_t)\) were collected from continuous records at 9-second intervals. For the analysis described here, only the first 60 pairs were used. We fit an ARV(2) model as described in 6.4.5. This data set is available as a text file.
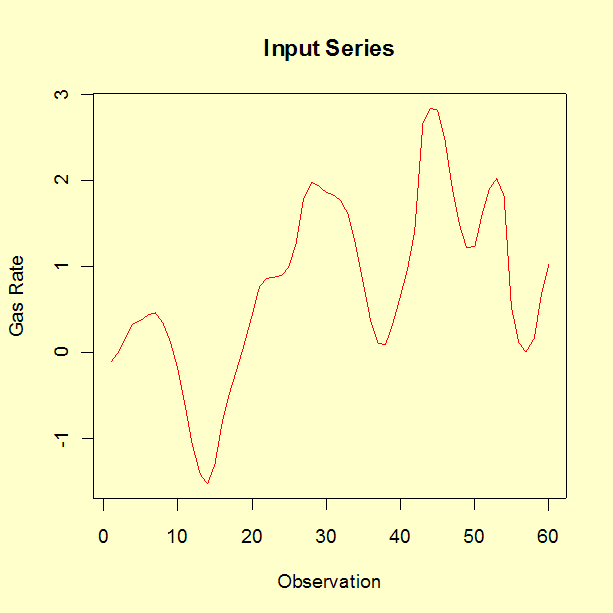
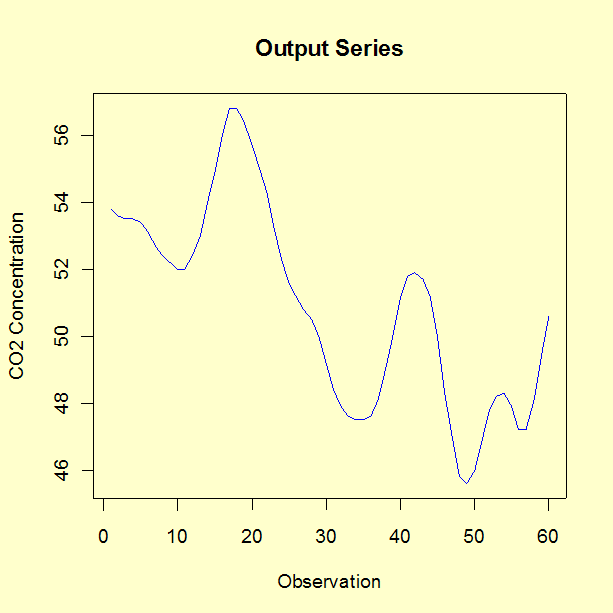
The parameter estimates for the equation associated with gas rate are the following.
Estimate Std. Err. t value Pr(>|t|)
a1t 0.003063 0.035769 0.086 0.932
φ1.11 1.683225 0.123128 13.671 < 2e-16
φ2.11 -0.860205 0.165886 -5.186 3.44e-06
φ1.12 -0.076224 0.096947 -0.786 0.435
φ2.12 0.044774 0.082285 0.544 0.589
Residual standard error: 0.2654 based on 53 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-Squared: 0.9387
Adjusted R-squared: 0.9341
F-statistic: 203.1 based on 4 and 53 degrees of freedom
p-value: < 2.2e-16
The parameter estimates for the equation associated with CO\(_2\) concentration are the following.
Estimate Std. Err. t value Pr(>|t|)
a2t -0.03372 0.01615 -2.088 0.041641
φ1.22 1.22630 0.04378 28.013 < 2e-16
φ2.22 -0.40927 0.03716 -11.015 2.57e-15
φ1.21 0.22898 0.05560 4.118 0.000134
φ2.21 -0.80532 0.07491 -10.751 6.29e-15
Residual standard error: 0.1198 based on 53 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-Squared: 0.9985
Adjusted R-squared: 0.9984
F-statistic: 8978 based on 4 and 53 degrees of freedom
p-value: < 2.2e-16
Box-Ljung tests performed for each series to test the randomness of the first 24 residuals were not significant. The \(p\)-values for the tests using CO\(_2\) concentration residuals and gas rate residuals were 0.4 and 0.6, respectively.
The forecasting method is an extension of the model and follows the theory outlined in the previous section. The forecasted values of the next six observations (61-66) and the associated 90 % confidence limits are shown below for each series.
90% Lower Concentration 90% Upper
Observation Limit Forecast Limit
----------- --------- -------- ---------
61 51.0 51.2 51.4
62 51.0 51.3 51.6
63 50.6 51.0 51.4
64 49.8 50.5 51.1
65 48.7 50.0 51.3
66 47.6 49.7 51.8
90% Lower Rate 90% Upper
Observation Limit Forecast Limit
----------- --------- -------- ---------
61 0.795 1.231 1.668
62 0.439 1.295 2.150
63 0.032 1.242 2.452
64 -0.332 1.128 2.588
65 -0.605 1.005 2.614
66 -0.776 0.908 2.593

